TOC
Open TOC
info
https://gfxcourses.stanford.edu/cs149
http://15418.courses.cs.cmu.edu/tsinghua2017/
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15418-s18/www/
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qT411g7n9
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV16k4y1z7z9
book
Is Parallel Programming Hard, And, If So, What Can You Do About It?
01 why parallelism
why
Power Density Wall

course themes
- Designing and writing parallel programs … that scale!
- Parallel computer hardware implementation: how parallel computers work
- Thinking about efficiency
02 basic arch
parallel execution
示例程序,利用泰勒公式计算 n 个数的正弦值
void sinx(int N, int terms, float* x, float* result) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { float value = x[i]; float numer = x[i] * x[i] * x[i]; int denom = 6; // 3! int sign = -1; for (int j = 1; j <= terms; j++) { value += sign * numer / denom; numer *= x[i] * x[i]; denom *= (2 * j + 2) * (2 * j + 3); sign *= -1; } result[i] = value; }}有如下并行的执行方式
- Multi-core: use multiple processing cores
线程级并发
使用 thread api,例如 pthreads,将 n 个数拆分给不同的 cpu 核心计算
- SIMD: use multiple ALUs controlled by same instruction stream (within a core)
单指令多数据并行
向量化,一次循环计算多个
// g++ -mfma main.cpp
#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <immintrin.h>
#define PI acos(-1)
void sinx(int N, int terms, float* x, float* result) { float three_fact = 6; // 3! for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 8) { __m256 origx = _mm256_load_ps(&x[i]); __m256 value = origx; __m256 numer = _mm256_mul_ps(origx, _mm256_mul_ps(origx, origx)); __m256 denom = _mm256_broadcast_ss(&three_fact); int sign = -1; for (int j = 1; j <= terms; j++) { // value += sign * numer / denom __m256 tmp = _mm256_div_ps(_mm256_mul_ps(_mm256_set1_ps(sign), numer), denom); value = _mm256_add_ps(value, tmp); numer = _mm256_mul_ps(numer, _mm256_mul_ps(origx, origx)); float fact = (2 * j + 2) * (2 * j + 3); denom = _mm256_mul_ps(denom, _mm256_broadcast_ss(&fact)); sign *= -1; } _mm256_store_ps(&result[i], value); }}
int main() { float x[8] = {PI, PI / 2, PI / 3, PI / 4, PI / 6, PI / 8, PI / 12, PI / 24}; float res[8]; sinx(8, 32, x, res); for (float re : res) { std::cout << re << std::endl; }}这里使用了 AVX intrinsics,在编译器优化下,也可能自动生成使用 AVX 指令的代码,详见 parallel101
对于出现分支语句,可以建立一个 bitmap,同时执行两条分支,对于不满足条件的分支,其执行的副作用不会反映到 cpu 中
- Superscalar: exploit ILP within an instruction stream. Process different instructions from the same instruction stream in parallel (within a core)
指令级并行
accessing memory
关注延迟 (latency) 和带宽 (bandwidth)
减少 latency 的方式
- 缓存 (caches)
- 预取 (prefetching)
- 多线程
主要讨论第三点,当某个线程出现 cache miss (processor stalls),可以切换到另一个线程执行,直到相应的数据出现在 cache 中
尽管该线程是 runnable 的,但为了 hide latency 且 increase throughput,进行了线程切换
Key idea of throughput-oriented systems:
Potentially increase time to complete work by any one any one thread, in order to increase overall system throughput when running multiple threads.
这里似乎并未区分 bandwidth 和 throughput
其代价是,需要额外的空间存储线程上下文信息,增加了单个线程执行的时间,尽管每个线程分到的 cache 空间会更少,但可以从内存中读取,在这一过程就可以进行线程切换,以达到 hide latency 的目的,这就对总线带宽提出了更高的要求
cpu 和 gpu 依赖不同的技术来减少 latency

03 prog models
核心问题 - Abstraction vs. Implementation
programming with ISPC
Intel SPMD Program Compiler (ISPC)
SPMD: single program multiple data
将上一节中的程序用 ISPC 改写
export void sinx( uniform int N, uniform int terms, uniform float* x, uniform float* result){ // assume N % programCount = 0 for (uniform int i=0; i<N; i+=programCount) { int idx = i + programIndex; float value = x[idx]; float numer = x[idx] * x[idx] * x[idx]; uniform int denom = 6; // 3! uniform int sign = -1; for (uniform int j=1; j<=terms; j++) { value += sign * numer / denom numer *= x[idx] * x[idx]; denom *= (2*j+2) * (2*j+3); sign *= -1; } result[idx] = value; }}一些要点
- uniform,标识符,代表所有的实例都有相同的值
- programCount,代表并发执行的实例数量
- programIndex,当前实例的下标
SPMD programming abstraction: 当执行到 ISPC 方法时,会生成 programCount 个实例并发执行这段代码
The ISPC gang abstraction is implemented by SIMD instructions on one core
所以 programCount 取决于硬件的 SIMD width
可以使用 foreach 关键字进一步简化上述程序
three parallel programming models
shared address space
线程之间通过读写共享变量进行通信
用于线程同步的变量也是共享变量
硬件实现的假设 - any processor can directly reference any memory location
由此诞生了 Symmetric (shared-memory) multi-processor (SMP),即每个处理器访问任何一块未被缓存的内存所用时间是一致的
也存在 Non-uniform memory access (NUMA),优化对局部内存的访问速度
message passing
联系网络传输中的 send 和 recv
实现通常使用 MPI (message passing interface)
实际上,实现了 MPI 的硬件也可以实现 Shared address space 抽象,反之亦然
Message passing 可以促使数据结构化,因为要尽可能减少消息传递的次数
data parallel
GPU 的主要设计思想
map(function, collection)function 即为无副作用的函数,collection 是一个其元素可以被独立处理的集合
类似函数式编程
其中两个重要的原语是 gather 和 scatter

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gather/scatter_(vector_addressing)
在实际环境中,这三种编程模型会混合使用
Use shared address space programming within a multi-core node of a cluster, use message passing between nodes
04 prog basics
一个并行程序是如何诞生的
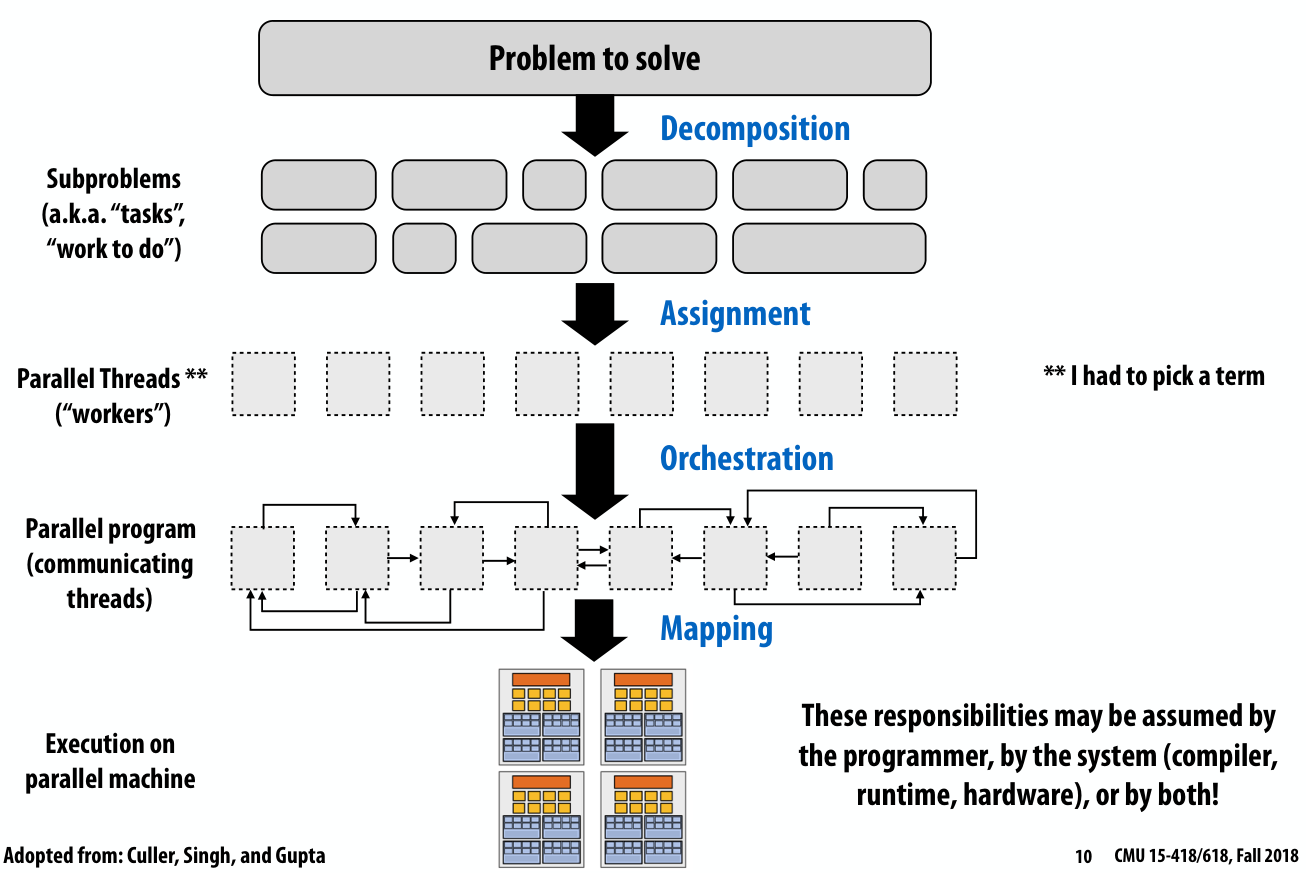
decomposition
Break up problem into tasks that can be carried out in parallel
Main idea: create at least enough tasks to keep all execution units on a machine busy
这里需要回顾 Amdahl’s Law,即一个程序的加速比取决于该程序中无法被并行执行部分的比例
下面会有一个例子讲解如何进行分解
assignment
Assigning tasks to threads
Goals: balance workload, reduce communication costs
注意,上述两个目标之间通常是不可兼得的
- 如果想要平衡工作负荷,在对具体数据和计算并不了解的前提下,最好的方案便是随机分配,然而这样 threads 之间的通信成本就会很大
- 如果想要减少通信成本,最好的方案便是将所有 tasks 分配给一个 thread
Assignment 通常分为两类,静态和动态
- 静态分配可以参考上一节中的 ISPC 程序,其中使用 programIndex 来标识每个 thread 应当执行哪些 tasks
- 动态分配可以参考 foreach 关键字,其具体的实现可能是维护一个 tasks 的 queue,每个 worker thread 执行其中未被执行的 tasks,维护这个 tasks queue 会有一定的开销

orchestration
编排
Goals: reduce costs of communication/sync, preserve locality of data reference, reduce overhead, etc
涉及到一些程序设计的细节问题,例如 threads 之间同步,结构化的通信,取决于具体的 programming model
mapping
这一步通常不需要程序员参与
-
mapping by the operating system
- map pthread to HW execution context on a CPU core
-
mapping by the compiler
- Map ISPC program instances to vector instruction lanes
-
mapping by the hardware
- Map CUDA thread blocks to GPU cores (future lecture)
有一些 mapping 上的决策问题,例如是将相关的 threads 映射到同一个处理器 (局部性,通信开销),还是将不相关的 threads 映射到同一个处理器 (平衡 workload)
example
A 2D-grid based solver
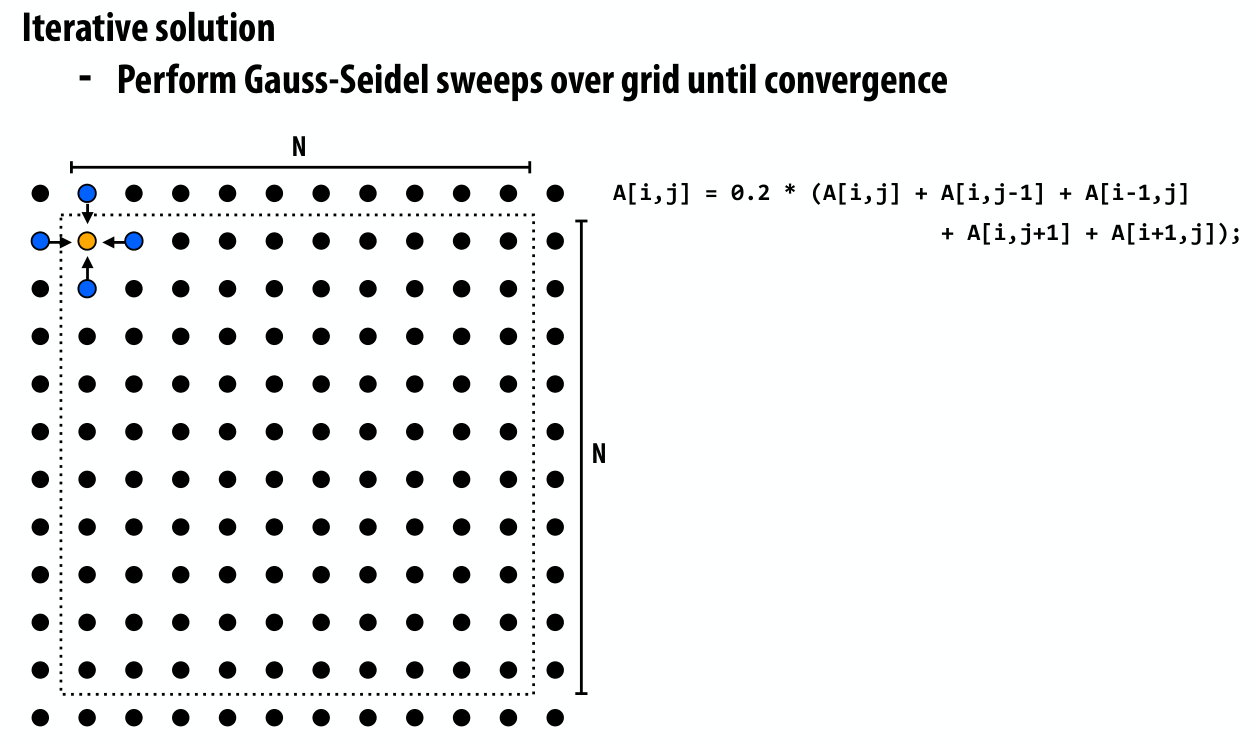
需要根据周围的网格计算自身的网格,直到整块区域收敛
decomposition
这里第一步就是要考虑如何分解,考虑到计算的顺序,最简单的想法便是按对角线方向依次更新,然而这样分解会出现不均匀的现象
下面给出了一种分解方案,先计算红色网格,然后计算黑色网格,这样依次进行

assignment
有两种候选方案

考虑到边界的网格计算会依赖其余 threads,所以显然第一种方案更理想
orchestration
首先考虑 Data parallel 模型,其伪代码如下

这里编排的细节大部分都由该 model 的具体实现处理了
再考虑 Shared address space 模型,其伪代码如下
int n; // grid sizebool done = false;LOCK myLock;BARRIER myBarrier;float diff[3]; // global diff, but now 3 copiesfloat *A = allocate(n+2, n+2);
void solve(float* A) { float myDiff; // thread local variable int index = 0; // thread local variable diff[0] = 0.0f; barrier(myBarrier, NUM_PROCESSORS); // one-time only: just for init while (!done) { myDiff = 0.0f; // perform computation (accumulate locally into myDiff) lock(myLock); diff[index] += myDiff; // atomically update global diff unlock(myLock); diff[(index+1) % 3] = 0.0f; barrier(myBarrier, NUM_PROCESSORS); if (diff[index]/(n*n) < TOLERANCE) break; index = (index + 1) % 3; }}有两处细节
- 引入局部的 myDiff,避免在计算的迭代中频繁加锁解锁
- 引入 diff 数组,减少 barrier 的个数
最后是 Message passing 模型,这里消息传递主要是边界的网格,以接收消息的 thread 为例
float* local_data = allocate(N+2,rows_per_thread+2);int tid = get_thread_id();int bytes = sizeof(float) * (N+2);// receive ghost row cells (white dots)recv(&local_data[0,0], bytes, tid-1);recv(&local_data[rows_per_thread+1,0], bytes, tid+1);// Thread 2 now has data necessary to perform future computation这里需要考虑 send 和 recv 的特性
- 若为阻塞,且所有的 threads 同时 send,就会触发死锁
- 在这种情形下,就要分奇偶来进行 send 和 recv
- 若为非阻塞,就不必考虑上述问题了
05 prog perf 1
Optimizing the performance of parallel programs is an iterative process of refining choices for decomposition, assignment, and orchestration…
Key goals
- Balance workload onto available execution resources
- Reduce communication (to avoid stalls)
- Reduce extra work (overhead) performed to increase parallelism, manage assignment, reduce communication, etc.
Tip: Always implement the simplest solution first, then measure performance to determine if you need to do better.
实现最简单的版本,以设立评估基线
workload balance
之所以要平衡工作负荷,本质原因是 Amdahl’s Law,imbalance 的部分即为无法并行执行的部分,会影响最大加速比
平衡 workload,实际上就是 assignment 的目标之一,通常分为两类,静态和动态
static assignment
当 workload 可预测时 (常数 / 线性),通常使用这种方案,可以减少运行时开销
实际上也存在 semi-static assignment 的方案,例如 N-Body simulation 中,workload 可以认为是计算一个星体需要考虑的其他星体的数量,随着时间推移,这个值会发生变化,所以可以在一段时间后重新根据新的数值 assignment
dynamic assignment
当 workload 不可预测时,通常使用这种方案,有一定的运行时开销,例如 work queue,在 shared address space 模型下,可以表达为
int N = 1024;// assume allocations are only executed by 1 threadint* x = new int[N];bool* is_prime = new bool[N];// initialize elements of x hereLOCK counter_lock;int counter = 0; // shared variablewhile (1) { int i; lock(counter_lock); i = counter++; unlock(counter_lock); if (i >= N) break; is_prime[i] = test_primality(x[i]);}即这里使用 lock 维护了一个 shared work queue
这里需要权衡的问题是 synchronization 的开销和完成一次 task 的开销
- 若 synchronization 的开销太大,synchronization 的部分即为无法并行执行的部分
- 若完成一次 task 的开销太大,就容易出现 workload imbalance 的情形
所以这里需要慎重的选择 task 的粒度 (granularity),这里就是一次 task 中需要对多少数执行素性检测
另一个问题是 long task 的分配,若 long task 在最后分配,仍然会出现 imbalance 的情形,如下图所示

若能够预先对 task 的大小有所了解,便可以优先 schedule long task,而 short task 放在最后去执行
除了 shared work queue,还存在 distributed work queues

这种方案的好处是减少了 synchronization 的开销,之所以不是避免开销,是因为在自己的 queue 空了之后,仍然需要从别的 queues 中获取 task,这其中存在 synchronization 开销
另一方面,也增加了 locality
回顾 ispc,其中 gang 抽象通常是 static assignment,而 task 抽象通常是 dynamic assignment
scheduling fork-join parallelism
fork 和 join 是一种常见的范式,例如,对于快速排序
// sort elements from ‘begin’ up to (but not including) ‘end’void quick_sort(int* begin, int* end) { if (begin >= end - 1) return; else { // choose partition key and partition elements by key, return position of key as `middle` int *middle = partition(begin, end); quick_sort(begin, middle); quick_sort(middle + 1, last); }}else 分支中的两个 quick_sort 就可以并发执行,主程序只需等待所有 quick_sort 线程 join 即可
为此,我们抽象出如下两个 api
cilk_spawncilk_sync
具体的语义可以参考 Programming in Cilk
于是上述程序可以改写为
void quick_sort(int* begin, int* end) { if (begin >= end - PARALLEL_CUTOFF) std::sort(begin, end); else { int *middle = partition(begin, end); cilk_spawn quick_sort(begin, middle); quick_sort(middle + 1, last); }}有两个要点
- 每个包含
cilk_spawn的程序最后都会有一个隐式的cilk_sync - 这里通过
PARALLEL_CUTOFF控制并发执行的阈值
最简单的实现就是将上述两个 api 映射到 thread api,然而这会产生大量的 threads,进而带来上下文切换的开销
fork
在 Cilk 的实现中,维护了一个 worker threads 的 pool,每个 pool 会尝试获取 work
这就引出一个问题,在 cilk_spawn 的过程中,thread 应该如何获取 work
下面定义两个术语

对于当前执行流所在的 thread,在 cilk_spawn 时有两种选择
- 执行 continuation,并将 spawned child 置入自己的 work queue,供其余 threads 窃取
- 执行 spawned child,并将 continuation 置入自己的 work queue,供其余 threads 窃取
举个例子,对于下述程序
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cilk_spawn foo(i);}cilk_sync;- 当先执行 continuation 时,work queue 中会依次存放
foo(0) ~ foo(N - 1),该 thread 最终会在cilk_sync处等待 - 当先执行 spawned child 时,work queue 中会依次存放
cont: i = 0,该 thread 会执行foo(0)
某种程度上来说,continuation first 类似 BFS,而 child first 类似 DFS
在 Cilk 的实现中,选择了 child first,原因如下
- continuation first 会显著增加 work queue 的大小
- child first 则可以让 long task 能够被优先调度
在具体实现上,work queue 会被实现为一个 lock-free dequeue,local thread 和 remote threads 在其两端获取 work
举个例子,对于上述快速排序,排序 1 ~ 200 时 local thread 的状态如下

remote threads 会优先从上端获取 work,而 local thread 在执行完后会从下端获取 work (locality)
join
下面考虑 sync 的实现,基本想法是为每个 fork-join 维护一些额外的信息

当 spawn == done 时,就代表所有的 spawned child 均已执行完毕
当 local thread 执行完 work 时,有两种策略
- stalling join policy
- greedy policy
具体的例子参考课件,在 Cilk 的实现中,选择了 greedy policy
06 gpu arch
建议观看 Kayvon Fatahalian 的版本
CUDA programming abstractions
thread hierarchy
threads are grouped into thread blocks
以如下程序为例
运行在 cpu 上的 host 代码
const int Nx = 12;const int Ny = 6;dim3 threadsPerBlock(4, 3, 1);dim3 numBlocks(Nx / threadsPerBlock.x, Ny / threadsPerBlock.y, 1);// assume A, B, C are allocated Nx x Ny float arrays// this call will trigger execution of 72 CUDA threads:// 6 thread blocks of 12 threads eachmatrixAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);运行在 gpu 上的 cuda device 代码,其执行类似 SPMD
// kernel definition__global__ void matrixAdd(float A[Ny][Nx], float B[Ny][Nx], float C[Ny][Nx]) { int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; C[j][i] = A[j][i] + B[j][i];}host code 可以在三个维度上指出每个维度上有多少 blocks,每个 blocks 中有多少 threads
在这里共 6 个 blocks,每个 blocks 中有 12 个 threads

address space
cudaMemcpy
在 host 和 device 的地址空间之间拷贝数据
message passing
- device memory model
per thread, per block (“shared”), or per program (“global”)

synchronization primitive
可以利用 per block shared memory 减少访问 device global memory 的开销
可能需要显式同步,以保证 block 中的 threads 能够正确的访问 block shared memory
shared address space
可以发现这里提供的抽象包含了之前提到的所有 parallel programming models
CUDA implementation on modern GPUs
需要注意 cuda 中的 thread 与 pthread_create 得到的 thread,在底层实现上并不相同
A compiled CUDA device binary includes
- program text (instructions)
- information about required resources
在这里假设共 8192 个 blocks,每个 blocks 中有 128 个 threads,每个 thread block 需要占据 520 字节的 block shared memory
GPU 中存在一个被称为 thread block scheduler 的硬件,负责动态的将 thread block 映射到硬件资源
需要补充 warp 的概念
On NVIDIA GPUs groups of 32 CUDA threads share an instruction stream
These groups called warps
Groups of 32 CUDA threads in a thread block are executed simultaneously using 32-wide SIMD execution
假设在如下的 GPU 中进行调度

那么每个 core 最多只能容纳两个 thread block,其中包含了 256 个 CUDA threads
两个 core 会依次执行 thread block,直到执行完所有的 thread blocks
这里还有一个假设
Major CUDA assumption: thread block execution can be carried out in any order (no dependencies between blocks)
注意这里分配 execution context 的基本单位是 block,而非 thread,这是因为如果使用了 synchronization primitive,thread 之间就可能存在 dependencies
也就是说,如果硬件的 execution context 不足以容纳一个 block,而 thread 之间又存在 dependencies,那么实际上 cuda device code 根本无法通过编译
Key implementation details:
- Threads in a thread block are scheduled onto same GPU core to allow fast communication through shared memory
- Threads in a thread block are are grouped into warps for SIMD execution on GPU hardware
07 prog perf 2
从 message passing 风格的 2D-grid based solver 引入
model of communication

在这种建模下,需要尽可能让 communication 的一部分能够与其他 work 并发执行,例如
- 异步的 send 和 recv 可以让 communication 与 computation 并发执行
- 考虑流水线化 communication,让 communication 之间并发执行

尽管 overhead 存在 buffered 的限制,系统的吞吐量仍然取决于 occupancy 的部分
two reasons for communication
inherent communication
Communication that must occur in a parallel algorithm. The communication is fundamental to the algorithm.
例如在 2D-grid based solver 的例子中,send 和 recv row 是 inherent communication
有一些指标量化 inherent communication
和
可以使用 arithmetic intensity 评估 2D-grid based solver 例子中的 assignment

显然 arithmetic intensity 越大越好,还存在一种更优的 assignment 方案,但是编码可能略复杂

artifactual communication
artifactual communication results from practical details of system implementation
- System might have a minimum granularity of transfer
- System might have rules of operation that result in unnecessary communication
- …
主要与 cache 的行为相关,回顾 cache misses 的场景
- Cold miss
First time data touched. Unavoidable in a sequential program.
- Capacity miss
Working set is larger than cache. Can be avoided/reduced by increasing cache size.
- Conflict miss
Miss induced by cache management policy. Can be avoided/reduced by changing cache associativity, or data access pattern in application.
- Communication miss (new)
Due to inherent or artifactual communication in parallel system.
有一些方法可以减少 artifactual communication
- 调整访存顺序

尽可能避免 capacity miss
- fusing loops

将多个循环合并
- sharing data
例如之前 cuda 里面利用 per block shared memory 减少访问 device global memory 的开销
contention

更多的内容参考课件
听不懂了……